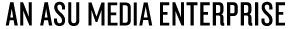Richard Lou, Border Door, 1988; Performance; Documentary photograph by James Elliot
Beyond debates over keeping statues up or tearing them down and changing the names of schools and streets lie more fundamental questions at the intersection of personal and public memory. We know how to honor and memorialize idealized heroes; we know less about remembering complicated, real people, who did extraordinary things—let alone how to remember historical figures who changed the world for the better but also contributed to systems of oppression. And we struggle to lift up the people and places that don’t appear in history books, or fit in with the bigger narratives of our shared past. How do we decide whom we remember and how? What do we owe those who lived before us, and those who will come after us? How can we expand our definition of monuments to include not just physical, public works, but other types of remembering?
Civil rights historian Daphne Chamberlain, visual and performance artist Richard Lou, and Patrick Weems, executive director of the Emmett Till Interpretive Center, visit Zócalo to discuss what public memory looks like in the 21st century, and how future generations might experience the act of looking back.
Zócalo invites our in-person audience to continue the conversation with our speakers and each other at a post-event reception with complimentary drinks and small bites.
“How Should Societies Remember Their Sins?” is a two-year editorial and event series supported by the Mellon Foundation. Blending scholarly essays and personal stories, we will explore how societies around the world collectively remember their transgressions and make attempts at repair, and how we might imagine new paths forward.
The Takeaway
There’s Power—and Promise—in Talking About Monuments
Doing Better By Future Generations Starts With Breaking Today’s Culture of Silence
“I get the feeling some people don’t want this conversation to happen,” said historian William Sturkey during last night’s public program at Two Mississippi Museums in Jackson, Mississippi. The framing …