
The mother of tweens was folding laundry at 5 a.m. before going to an early spinning class when the phone rang. It was early October 2009 and Carol Greider, a biologist at Johns Hopkins University, picked up and heard a voice from Stockholm. She had won that year’s Nobel Prize in medicine.
Despite Greider’s accomplishment—she earned the award for discovering telomerase, an enzyme of huge relevance in aging and cancer—it is this image of her making use of every waking minute that has stuck with me four years later. It is an image that I deeply identify with, not because I’m a scientist, but because I’m a woman juggling family and career. The mental picture helped me understand Greider as a flesh-and-blood mortal, not a superwoman whose lofty level of achievement I could never aspire to.
Unfortunately, Greider remains a rarity in the pantheon of Nobel scientists. And that’s partly because we haven’t done enough to help young female scientists balance the demands of academic research with the pull of family responsibility. That needs to change.
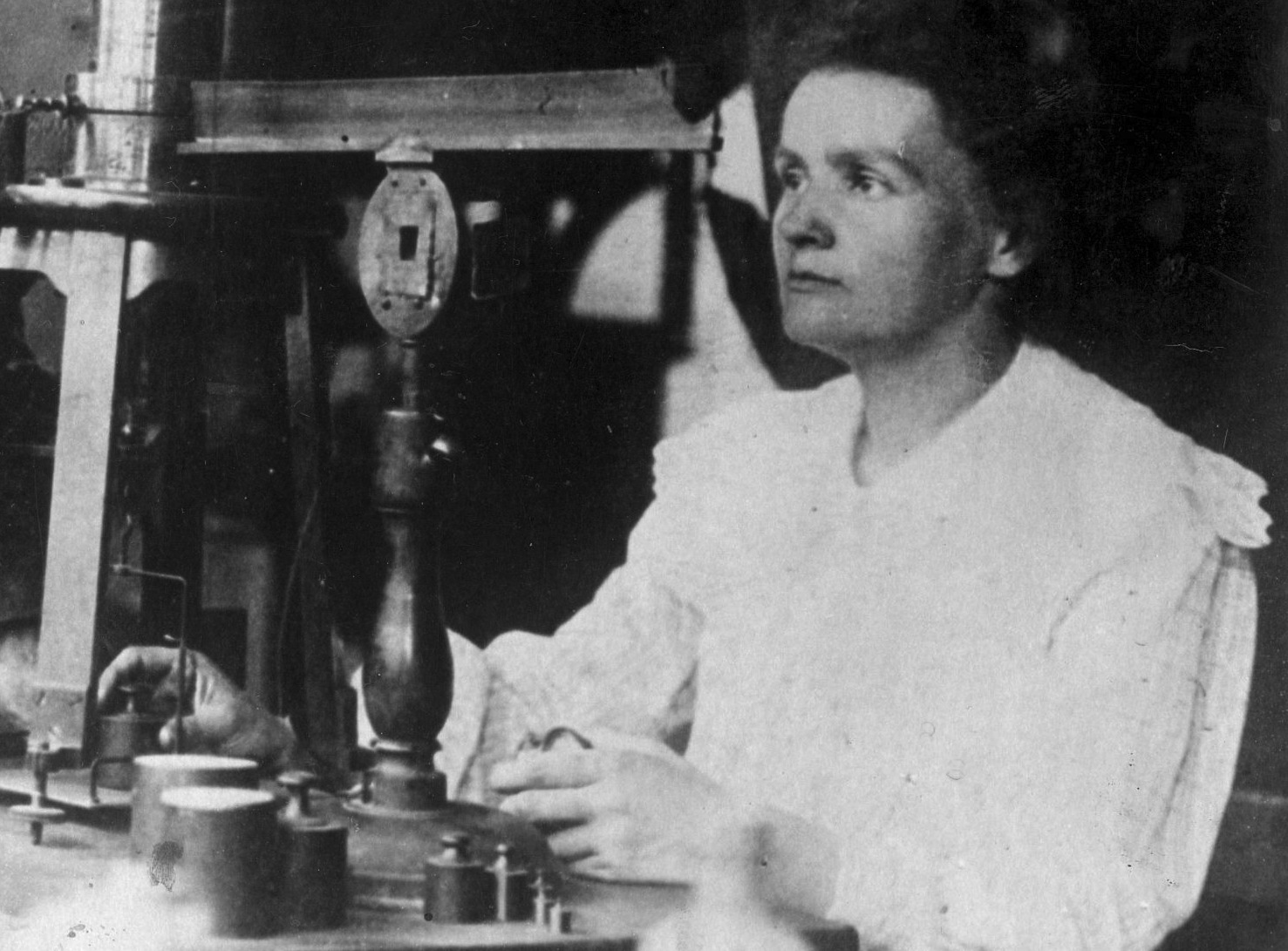
Admittedly, today’s situation is better than it was when Greider entered grad school in the early 1980s, never mind in the dark days of the preceding decades. Then, when women were scarcely to be found at undergraduate lab benches, the results in the rarefied reaches of Stockholm couldn’t help but be dismal. Since the awards were launched in 1901, two physics laureates have been women: Marie Curie in 1903 and Maria Goeppert Mayer in 1963. In chemistry, four of the 165 winners have been women. (Marie Curie was one of them, in 1911; she is the only woman to have won two Nobels.) Women have won 5 percent of the coveted awards in physiology or medicine. And it was 2009 before Elinor Ostrom, of Indiana University and Arizona State University, became the first-ever female laureate in economics.
In fact, 2009 was something of a banner year for women—Greider shared her award with her mentor, Elizabeth Blackburn, of the University of California at San Francisco, and Israel’s Ada Yonath shared the prize in chemistry. Since then, men have continued to sweep the science awards.
To be a female Nobel winner has not only required brilliance, but also preternatural determination in the face of cultural, social, and political obstacles. The Italian neurologist Rita Levi-Montalcini secretly conducted experiments in her bedroom in Mussolini’s Italy. Francoise Barre-Sinoussi, the Parisian who co-discovered the AIDS virus—and whose father thought a woman’s place was in the home—was in the lab on her wedding day. Her fiancé had to call her to remind her to turn up at the ceremony. Barbara McClintock, the U.S. geneticist who won the prize in 1983, was nearly prevented from attending college by her mother. She was afraid higher education would make her daughter unmarriageable.
All this was decades ago, before recent campaigns to encourage more young women to choose careers in STEM (science, technology, engineering, and math)—not to mention, in the U.S., before the Civil Rights Act, affirmative action, and Title IX. What’s the excuse in 2013?
One partial explanation for the bleak numbers: The awards often honor discoveries made decades earlier. Even today, that means spotlighting accomplishments from a time when female scientists were a rarity. Take the 2013 prize in physiology or medicine, which was awarded earlier this month to James Rothman, Randy Schekman, and Thomas Südhof for their work teasing out the micro-mechanisms that allow cells to transport their molecular cargo to specific destinations. Their key papers in this area were published between 1979 and 1993.
Still, while it may be tempting to conclude that just a little more patience is required before a raft of lady laureates take Stockholm by storm, it’s important to note that promising numbers in biology, where by 2010 U.S. women were collecting 53 percent of Ph.D.s, don’t translate to other disciplines: That same year, women earned 39 percent of chemistry doctorates, 34 percent of economics doctorates, and 20 percent of physics doctorates.
What’s more, systemic issues are holding women back across the sciences, meaning that we may not see more female laureates by simply funneling more and more women through Ph.D. programs. The hard truth is that women with brand new doctorates—so called post-docs—enter their prime childbearing years exactly as they encounter the make-or-break time when they must compete for tenure-track positions. The competition is brutal, the hours in the lab never-ending—and the attrition of women is far higher than that of men. A 2009 survey of post-doctoral scientists from all disciplines in the University of California system found that women who had children after they earned Ph.D.s were twice as likely as male postdocs—or their female peers with no children and no plans to have them—to drop their goal of becoming a research professor.
What, specifically, should institutions do to offer such support? Universities can make meaningful policy changes, like allowing women with young children to stop the tenure clock for a period of time—an option available at some, but not all academic centers. They should ensure that young, female scientists have dedicated, top-notch mentors. And they can provide all-important maternity and parental leave to young, striving scientists.
Federal agencies also have a role to play. Big funders, led by the National Institutes of Health, have already implemented policies like no-cost grant extensions that allow scientists with family obligations extra time to complete a project, and others that allow fellowship periods to be extended or deferred for childcare purposes. But agencies can, and should, do more. One task the government is especially suited to is longitudinal data collection on those family-friendly policies—which isn’t now collected systematically. Without this information, we can’t know what policy changes are working, and which ones aren’t.
If we want top-drawer women to stay in science careers—and this country, beset by daunting, and growing, global science competition, could certainly use them—institutions of all stripes need to show a far more serious commitment to supporting them.
To put it another way, if we want to see more women celebrating in Stockholm, we should strive to build a world in which the likes of Carol Greider are hardly ever to be found folding the laundry at 5 in the morning.



Send A Letter To the Editors